Podziemne Sekrety Hiszpanii
Hiszpania, znana z pięknych plaż i słonecznego wybrzeża, skrywa również fascynujące tajemnice pod powierzchnią ziemi. Jednymi z najbardziej fascynujących elementów geologicznych kraju są płyty tektoniczne i majestatyczne góry, które nie tylko kształtują krajobraz, ale także wpływają na historię, kulturę i ekologię Hiszpanii.
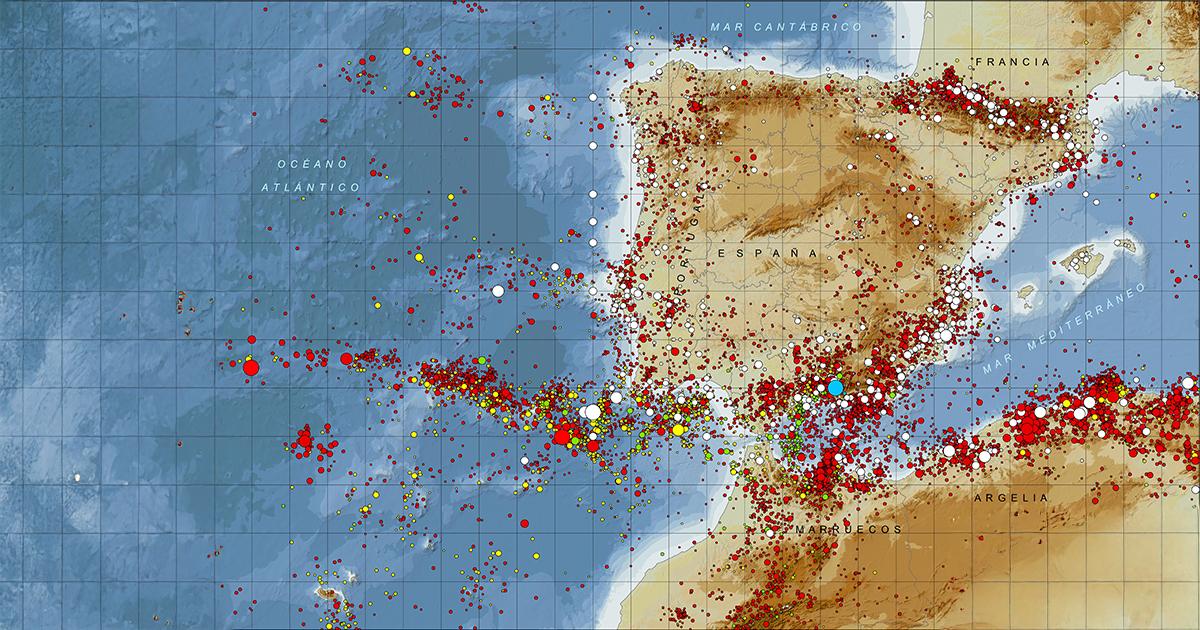
Płyty tektoniczne to ogromne fragmenty skorupy ziemskiej, które poruszają się na gorącym, płynnym płaszczu ziemskim. Ich ruchy, choć niewidoczne dla naszych zmysłów, mają ogromny wpływ na geologię, sejsmologię i geografię naszego globu. Hiszpania leży na styku dwóch głównych płyt tektonicznych: płytce iberyjskiej i płytce afrykańskiej. Granica między płytami, znana jako rów wschodnio-hiszpański, jest miejscem aktywnej sejsmicznie, co może prowadzić do trzęsień ziemi.
W ciągu wieków Hiszpania doświadczyła wielu trzęsień ziemi, których przyczyną były często ruchy płyt tektonicznych, na których leży kraj. Szczególnie aktywny sejsmicznie jest obszar południowej Hiszpanii. W tym regionie często występują trzęsienia ziemi o różnych skalach, które mogą powodować znaczne zniszczenia materialne oraz wpływać na życie i bezpieczeństwo mieszkańców.
Największe trzęsienie ziemi w historii Hiszpanii miało miejsce 25 grudnia 1884 roku i miało epicentrum w miasteczku Arenas de Rey, leżącym w regionie Andaluzji. Trzęsienie to osiągnęło szacowaną magnitudę 6,5-7,0 i było jednym z najpotężniejszych w historii kraju. W wyniku tego trzęsienia ziemi, obszar Andaluzji został dotknięty znacznymi zniszczeniami, a wiele miejscowości, w tym Arenas de Rey, zostało niemal doszczętnie zniszczonych. Szacuje się, że śmierć poniosło około 1 000 osób, a tysiące zostały rannych.
To tragiczne wydarzenie spowodowało również znaczne zmiany w podejściu do budownictwa i przepisów dotyczących bezpieczeństwa budowlanego w Hiszpanii. Stało się przestrogą przed potencjalnymi zagrożeniami sejsmicznymi w kraju i skłoniło do podejmowania działań na rzecz zwiększenia świadomości i przygotowania społeczności na wypadek ewentualnych trzęsień ziemi.
Choć ruchy płyt tektonicznych mogą być przyczyną trzęsień ziemi i innych katastrof, to jednocześnie prowadzą do powstawania niezwykłych i pięknych form terenowych, które są częścią bogatej geologicznej historii Hiszpanii. To właśnie im zawdzięczamy powstanie pasm górskich, takich jak Pireneje na północy i Sierra Nevada na południu kraju.
Góry Hiszpanii oferują niezwykłą różnorodność krajobrazów, od skalistych szczytów po malownicze doliny i klify. Na północy kraju znajdują się majestatyczne Pireneje, które tworzą naturalną granicę między Hiszpanią a Francją, oferując nie tylko doskonałe warunki do uprawiania sportów zimowych, ale także spektakularne widoki i trasy turystyczne.
Na południu Hiszpanii dominują góry Sierra Nevada, które są najwyższym łańcuchem górskim w kraju. Ich szczyt Mulhacén sięga ponad 3 400 metrów n.p.m. i jest to jedno z najbardziej popularnych miejsc w Hiszpanii dla miłośników trekkingu, wspinaczki i narciarstwa.